Your Gateway to Crypto Wallet
You’ve heard about crypto wallets, but what exactly are they? Whether you’re just stepping into the world of digital currencies or you’ve already bought your first crypto coin, understanding cryptocurrency wallets is your essential starting point.
A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool that lets you store, send, and receive crypto like Bitcoin or Ethereum. It doesn’t actually “hold” coins, but manages the keys that prove ownership. Crypto wallets can be software or hardware-based, hot or cold, and custodial or non-custodial.
What Is a Cryptocurrency Wallet?
At its core, a cryptocurrency wallet is a digital wallet that allows you to access and manage your crypto assets. Unlike a physical wallet that holds cash, a crypto wallet stores the private keys that give you access to your digital currencies. Those keys are what you use to authorize transactions on blockchain networks like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or Solana.
Think of it like your email account: the public address is like your email address (you can share it), and your private key is your password (you never share it). Lose the private key, and you’ve lost access to your funds.
A Wallet for Every Level
Whether you’re holding $50 in stablecoins or managing millions in crypto, your choice of wallet determines how secure and accessible your assets are.
- Hot wallets are connected to the internet—great for speed, but they carry more risk.
- Cold wallets store keys offline—less convenient but ultra-secure.
- Custodial wallets are managed by third parties (like crypto exchanges).
- Non-custodial wallets give you full control—but also full responsibility.
You’ll learn the differences between these types, how to choose the right one, and when to upgrade your security.
Why It Matters More Than Ever
Crypto isn’t just an investment anymore—it’s a way to shop, get paid, and interact in Web3 environments. That means your wallet isn’t just a vault—it’s a gateway to a new financial ecosystem.
And when you’re managing high-value assets, trust and security aren’t optional.
Advanced Tip: Crypto Wallet vs. Account
Many beginners confuse wallets with exchange accounts—but they’re not the same. When you hold crypto on an exchange, you don’t truly own it.
An exchange owns the keys—you’re trusting a third party. With a wallet (especially a non-custodial one), you own your private keys, and therefore your assets.
Why Trust Matters: Deffio’s Edge
Deffio operates under an EU-licensed VASP (Virtual Asset Service Provider) framework—meaning we comply with strict regulatory standards around wallet creation, user verification, and transaction security. Whether you’re an individual user or a business integrating crypto payments, Deffio’s infrastructure gives you peace of mind.
We’re not just about wallet tools—we’re about trusted crypto access.
Whether you’re just exploring crypto or managing a diversified digital asset portfolio, your wallet is your foundation. In this guide, you’ll learn how to protect it, optimize it, and use it to unlock new financial possibilities.
Blockchain Fundamentals: Building Your Crypto Knowledge
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. Each group of transactions forms a block, and these blocks link together in a secure, chronological chain. Blockchain technology ensures transparency, trust, and security without needing banks or intermediaries, making it the foundation of cryptocurrencies and crypto wallets.
Why Should You Care About Blockchain?
Ever asked, “Hey Google, explain what is blockchain?” Here’s the simple version:
Blockchain technology is what makes cryptocurrencies work. It’s the invisible engine behind your digital wallet, powering secure transactions, eliminating middlemen, and recording ownership in real time. If you’re using a crypto wallet, you’re already relying on blockchain—even if you don’t realize it.
How Does Blockchain Actually Work?
Think of blockchain as a digital notebook that’s copied to thousands of computers around the world. When someone makes a transaction, that data is bundled into a block. Each block includes:
- A timestamp
- Transaction data
- A reference to the block before it
These blocks connect—forming a chain that’s nearly impossible to tamper with.
The Big Picture
Blockchain isn’t just about Bitcoin. It’s transforming everything from finance to healthcare. And when you use a crypto wallet, you’re tapping into this powerful technology—one block at a time.
Understanding Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Origins
Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, created in 2008 by an anonymous figure named Satoshi Nakamoto. It introduced a decentralized, peer-to-peer digital money system that uses cryptography for security. Bitcoin paved the way for crypto wallets by requiring users to manage private keys to access and control their digital assets.
Who Created Bitcoins—and Why?
If you’ve ever asked, “Who created bitcoins?” the answer points to Satoshi Nakamoto, a mysterious developer (or group) who released the original Bitcoin whitepaper in 2008. Nakamoto’s goal was simple yet revolutionary: to build a trustless monetary system—digital money that didn’t rely on banks or governments.
Bitcoin went live in 2009. It used blockchain technology and cryptography to allow people to send and receive value without a middleman. No bank approvals. No centralized control. Just code and consensus.
Why Is Bitcoin So Important for Wallets?
Bitcoin’s creation led to the first cryptographic wallets. Since there’s no physical coin, users need a secure way to store their private keys—the only way to access their bitcoins. This need gave birth to crypto wallets, which manage your keys and interact with the Bitcoin blockchain.
Your crypto wallet doesn’t store bitcoins directly—it stores the credentials that let you spend or transfer them. If you lose your private key, you lose your coins forever.
What Is Cryptography Currency?
A cryptography currency (a less common term for cryptocurrency) uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control asset ownership. This security model is the backbone of every crypto wallet—ensuring only you can authorize movements of your funds.
Popular Cryptocurrencies and Their Wallets
With thousands of digital assets on the market, it’s easy to get overwhelmed. But understanding just a few key cryptocurrencies—and the wallets they pair with—can give you a strong foundation in managing your crypto securely and effectively.
What Are Dogecoins?
Dogecoins are a type of cryptocurrency that began as a joke but became popular for tipping and online transactions. Based on the Shiba Inu meme, Dogecoin has grown into a real digital currency supported by an active community. It runs on its own blockchain and needs compatible wallets like MultiDoge or Dogecoin Core.
Originally created in 2013 as a lighthearted parody of Bitcoin, Dogecoin (DOGE) quickly gained traction thanks to its friendly branding, low transaction fees, and viral internet appeal. Despite its origins, Dogecoin now holds billions in market cap and is accepted by various merchants.
What Is a Meme Coin?
Meme coins are cryptocurrencies inspired by internet culture, memes, or social trends. While Dogecoin was the first, it’s not the only one—Shiba Inu (SHIB), Pepe (PEPE), and others followed.
Meme coins are often volatile and highly speculative. Still, many users buy and trade them using standard crypto wallets like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or centralized exchange wallets.
Pro Tip: Always verify if a wallet supports the specific blockchain your meme coin is built on (e.g., Ethereum, BNB Chain).
What Is Ether Currency?
Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain. It’s used to pay for smart contract operations and transaction fees. Ether currency powers decentralized applications and services across Web3. Wallets like MetaMask and Ledger are popular for managing ETH and tokens built on Ethereum.
Launched in 2015, Ethereum expanded the use of blockchain beyond just money. Its smart contracts enabled decentralized apps (dApps), DeFi services, and NFT platforms. Today, Ether (ETH) is the second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap and a key driver of Web3 innovation.
Which Wallet Should You Use?
Your wallet choice should align with the type of cryptocurrency you hold. For example:
Bitcoin holders prefer Electrum, BlueWallet, or Ledger for security.
Ethereum and meme coin users go with MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or hardware options.
Dogecoin users often start with MultiDoge or Dogecoin Core.
Always choose a wallet that supports the specific blockchain of your crypto asset—not all wallets work with all coins.
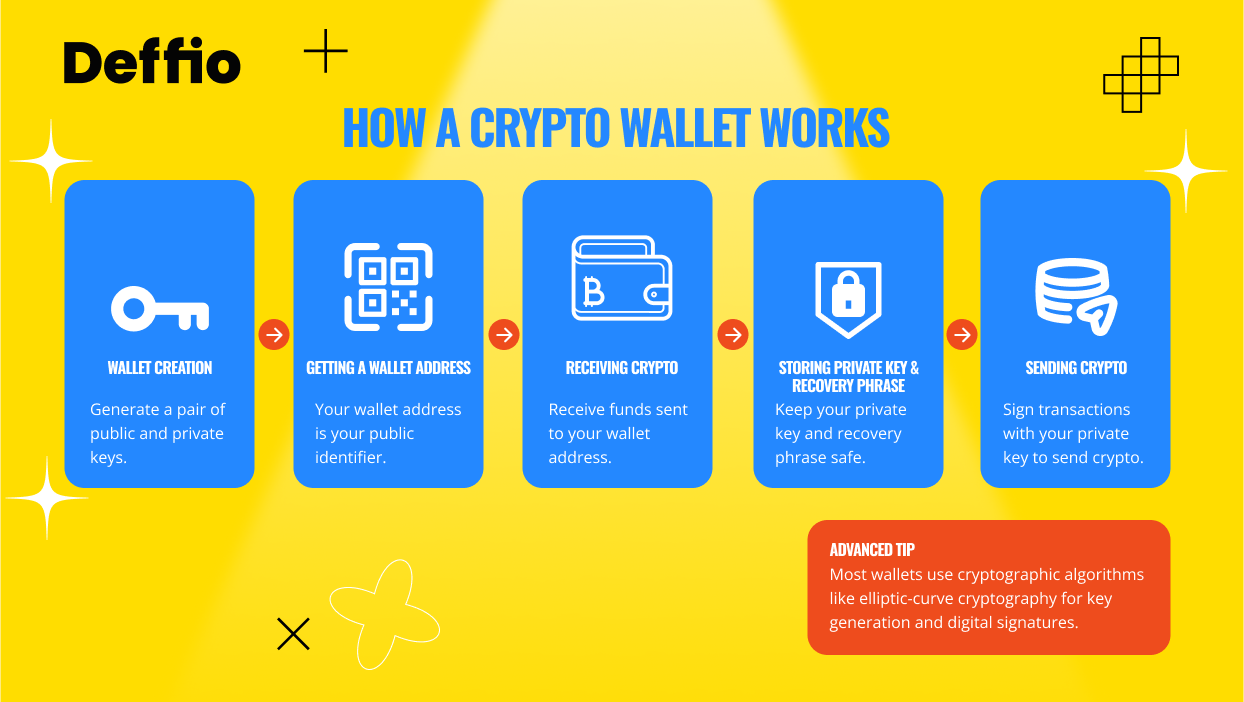
Crypto Wallet Fundamentals
What Are Crypto Wallets?
A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool that stores your private keys and lets you send, receive, and manage crypto assets. It doesn’t hold coins physically—instead, it grants access to your funds on the blockchain. Wallets come in many forms, from mobile apps to hardware devices, and protect your assets through advanced encryption.
How Do Crypto Wallets Work?
Think of a cryptocurrency wallet like a digital version of your physical wallet—but smarter and more secure. Instead of holding cash, it stores the private and public keys that prove ownership of your crypto. When you make a transaction, your wallet signs it with your private key and broadcasts it to the blockchain.
There are two basic functions your wallet performs:
- Access – You can check balances or send/receive assets from blockchain addresses.
- Authentication – Every transaction is signed with your private key to prove it’s really you making the move.
What Is a Wallet Address?
A wallet address is a string of characters that represents your public key—it’s what you share to receive crypto. Like an email address for crypto, each address is unique to your wallet. Example: 0xF123…789c.
You can generate multiple wallet addresses within the same wallet, each tied to different coins or tokens. It’s one of the most important identifiers in crypto.
Crypto Wallet vs. Traditional Wallet
A traditional wallet stores physical money and cards. A digital wallet, in the crypto sense, doesn’t store the money itself—it stores the keys to unlock that money on a decentralized blockchain. No banks. No gatekeepers. Just cryptographic control over your assets.
How Crypto Wallets Work
To truly understand how to use and secure a cryptocurrency wallet, you need to grasp three core elements: keys, recovery phrases, and the wallet setup process. In this section, you’ll learn what happens behind the scenes when you create a wallet—and how to keep it secure.
Public Key vs. Private Key: What’s the Difference?
A public key is like your wallet’s address—others use it to send you crypto. A private key is your secret password that authorizes transactions. You must protect your private key at all costs. Together, these keys ensure only you can access and control your crypto assets on the blockchain.
Public Key
Your public key is generated from your private key and can be freely shared. It’s the cryptographic foundation for your wallet address, and it’s what others use to send you funds.
Private Key
The private key is the master key to your crypto. Stored in your wallet, it’s what signs transactions and proves ownership. If someone else gets your private key, they can drain your wallet—no recovery possible.
What Is a Recovery Phrase?
A recovery phrase, also known as a seed phrase or 12-word recovery phrase, is a human-readable backup of your private keys. If you lose your device or app, this phrase is the only way to recover your cryptocurrency wallet and funds. Keep it offline and safe.
When you create a wallet, you’re shown a set of 12 or 24 random words. This is your recovery phrase—and it’s the most important part of your wallet setup.
Each word in the phrase maps to part of your private key using an algorithm called BIP39. With this phrase, anyone can regenerate your entire wallet. That’s why you must:
- Write it down (not on your phone or cloud)
- Store it in a fireproof, waterproof place
- Never share it with anyone
Pro Tip: If a wallet ever asks you to enter your 12-word recovery phrase outside the original app or device, it’s likely a phishing attack.
How to Create a Crypto Wallet: Step-by-Step
To create a crypto wallet, download a wallet app, follow the setup instructions, and securely back up your recovery phrase. Your wallet will generate a private/public key pair to access and manage your crypto. Never skip the backup step—your phrase is your lifeline.
Step-by-Step Wallet Setup
- Choose a wallet type
Download a software wallet (like MetaMask or Trust Wallet) or set up a hardware wallet (like Ledger or Trezor). - Install and launch the wallet
Follow on-screen instructions to begin setup. You may be prompted to choose between creating a new wallet or restoring one. - Generate your recovery phrase
The app will display your 12-word recovery phrase. Write it down carefully. This is your only backup. - Confirm the phrase
You’ll be asked to re-enter the phrase to ensure you saved it correctly. - Create a password or PIN
This adds a layer of protection for daily access. Think of it as locking the app—not the actual keys. - Receive your wallet address
Now you’re ready to receive crypto. You’ll be given a wallet address, derived from your public key.
How to Secure Cryptocurrency Wallets
To secure a cryptocurrency wallet, keep your private key and 12-word recovery phrase offline and never share them. Use hardware wallets for large amounts, enable two-factor authentication, and avoid storing sensitive data on cloud apps. Only use trusted wallets and always verify URLs and apps to avoid phishing or scams.
Best Practices:
- Use cold storage (offline wallets) for large amounts
- Enable two-factor authentication for exchange-linked wallets
- Never store recovery phrases in digital format (like screenshots or cloud notes)
- Check URLs—fake wallet sites are a common attack vector
Crypto wallets give you complete control—but with that control comes responsibility. Master the basics of keys, phrases, and setup now, and you’ll be far ahead of the average user.
Getting Your First Crypto Wallet
To get a cryptocurrency wallet, download a trusted app like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or Deffio on your phone or desktop. Follow the setup steps, write down your recovery phrase, and your wallet will generate a public address. Choose a wallet that supports your crypto type and fits your platform—iPhone, Android, or desktop.
What’s the Best Way to Get a Wallet for Cryptocurrency?
If you’ve searched “how to get wallet for cryptocurrency,” you’re not alone. It’s one of the first steps into the crypto world. The best way to get started is to pick a wallet that fits your platform and goals—mobile-first apps for speed and ease, or desktop/hardware options for stronger security.
Platform-by-Platform Wallet Options
iPhone (iOS)
Looking for the best crypto wallet for iPhone or iOS? Here are top choices:
- MetaMask – Great for Ethereum and Web3 users
- Trust Wallet – Multi-chain support and user-friendly
- Deffio App (Coming Soon) – Built with compliance-first wallet infrastructure for safer, regulated access
🛡️ Deffio Insight: As an EU-licensed VASP, Deffio ensures all wallet interactions meet strict financial compliance rules. That’s why businesses and individuals alike trust us for secure custody options.
Android
- Trust Wallet – Broad compatibility and staking options
- Atomic Wallet – Includes a built-in DEX (Decentralized Exchange)
- Exodus – Clean UI and supports 260+ assets
Desktop
- Exodus Desktop – For multi-asset management
- Electrum – Lightweight wallet for Bitcoin only
- Deffio Web Wallet (B2B Focused) – Ideal for enterprise-grade wallet orchestration
Step-by-Step: Setting Up Your First Crypto Wallet
- Choose Your Wallet App
Visit the official website or app store. Always verify URLs to avoid phishing. For example:- MetaMask: https://metamask.io
- Trust Wallet: https://trustwallet.com
- Download and Install
Install the app on your device (iOS, Android, or desktop). Give required permissions if prompted. - Create a New Wallet
Select “Create Wallet.” Some apps will also offer to import an existing wallet. - Backup Your Recovery Phrase
You’ll receive a 12-word recovery phrase. Write it down and store it offline—this is your only way to recover the wallet if your device is lost or stolen. - Set Up PIN or Password
Add an extra layer of protection by setting a secure password, PIN, or biometric login. - Access Your Wallet Address
After setup, your wallet address (public key) will be generated automatically. This is what you’ll share to receive funds.
First-Time User Recommendations
If you’re new to crypto, here are a few best practices:
- Start with a mobile wallet like Trust Wallet or MetaMask
- Buy small amounts first to get used to transactions
- Only download wallets from verified sources
- Avoid browser extensions unless you understand the risks
Why Deffio Wallet Infrastructure Stands Out
Whether you’re a casual investor or a business integrating crypto payments, wallet security is non-negotiable. Deffio’s VASP-compliant wallet infrastructure offers scalable, secure wallet provisioning that meets the needs of:
- Enterprises managing multiple user wallets
- Platforms integrating crypto payment flows
- Users needing regulated environments with recovery and audit features
Now that you’ve got your wallet set up, you’re ready to explore the differences between wallet types—and how to choose what’s right for your use case.
Types of Crypto Wallets
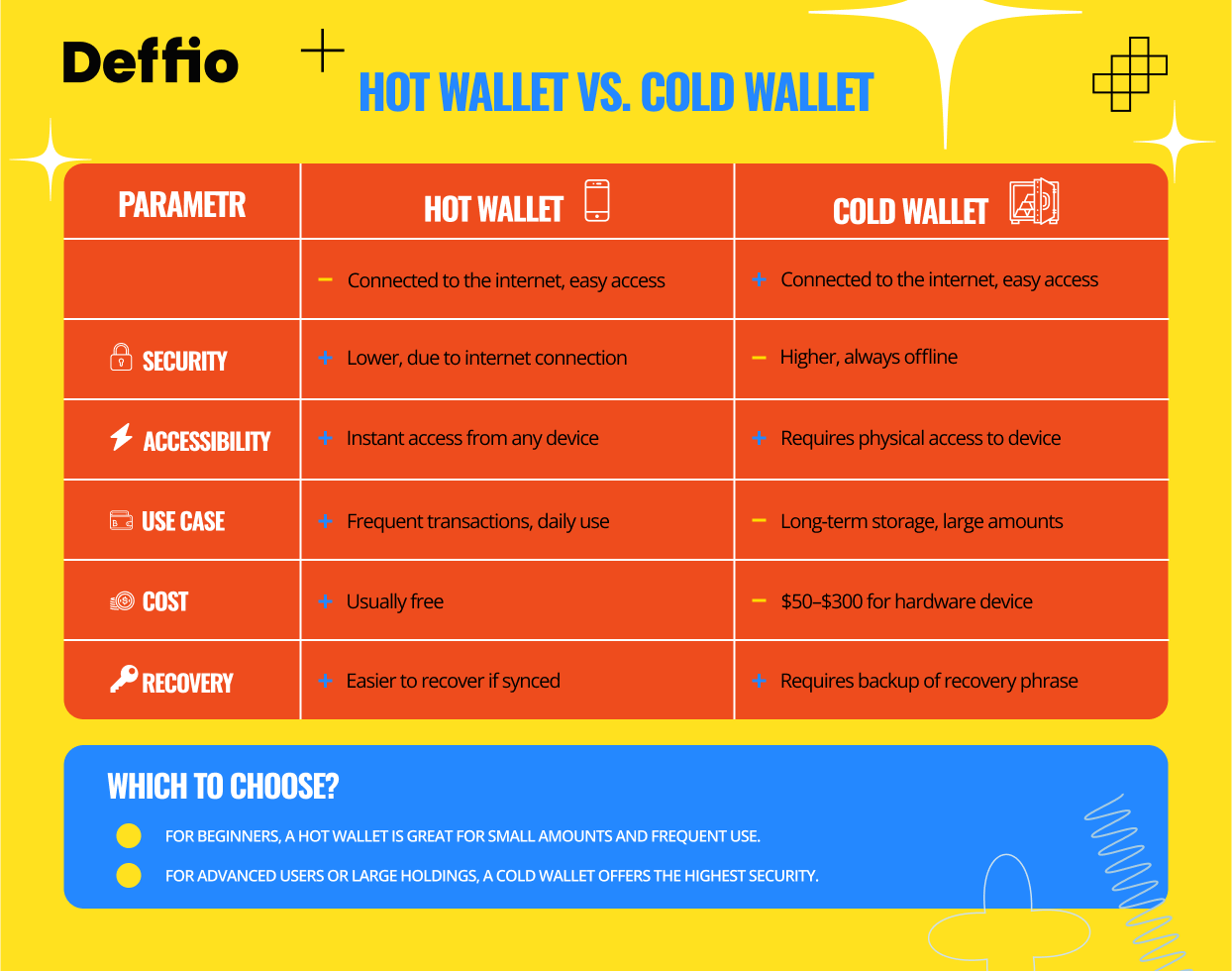
Hot Wallets vs. Cold Wallets
A hot wallet is connected to the internet and used for frequent crypto transactions. A cold wallet is offline and offers higher security, often used for long-term storage. Hot wallets are convenient but more vulnerable to hacks, while cold wallets are less convenient but ideal for protecting large holdings.
What Is a Hot Wallet?
A hot wallet is any cryptocurrency wallet that remains connected to the internet. This includes mobile apps, desktop software, browser extensions, and exchange wallets. Since they’re always online, hot wallets allow for quick access and real-time transactions—but that convenience comes with increased exposure to cyber threats.
Examples of hot wallets:
- MetaMask (browser/mobile)
- Trust Wallet (mobile)
- Coinbase Wallet (mobile)
What Is a Cold Wallet?
A cold wallet refers to any crypto storage method that remains offline most or all of the time. Think of it as a digital safe that’s not plugged in unless needed. Cold wallets are preferred for long-term holders and institutional investors.
Examples of cold wallets:
- Ledger Nano X (hardware)
- Trezor Model T (hardware)
- Paper wallets (manually stored keys)
How Are Cryptocurrency Hot Wallets Different from Cold Wallets?
Hot wallets are “live” tools—they’re always connected to blockchain networks, which is why they’re faster but less secure. Cold wallets are like putting your coins in a vault. They’re immune to most hacks because they’re disconnected from the internet.
Use Case Scenarios
Hot Wallet Example:
You’re buying NFTs on OpenSea or swapping tokens on Uniswap. You’ll want a hot wallet like MetaMask that connects directly to these platforms for seamless interaction.
Cold Wallet Example:
You’ve invested $25,000 in Bitcoin and don’t plan to touch it for a year. A hardware wallet like Ledger is ideal—you store the keys offline and only connect when transferring funds.
Security Implications: Hot vs Cold
Hot Wallet Risk: Phishing attacks, browser vulnerabilities, or malware can steal your keys. Even exchanges with hot wallet systems have been hacked.
Cold Wallet Protection: Because it’s offline, even if your PC is compromised, your keys are not. Unless someone physically steals your hardware wallet and PIN, your funds are safe.
This distinction is essential as your crypto portfolio grows. In the next section, we’ll explore custodial vs. non-custodial wallets, another key decision every crypto user must make.
Hardware Wallets Deep Dive
A hardware wallet is a physical device that securely stores your crypto private keys offline. It’s one of the safest ways to protect digital assets from online threats. Hardware wallets like Ledger or Trezor are ideal for long-term holders and those storing large amounts of cryptocurrency.
What Is a Hardware Wallet?
Hardware wallets explained: They are specialized devices built to store private keys offline, keeping them isolated from internet-connected devices. This protects against common threats like malware, phishing, and remote hacking.
Unlike software wallets (apps or browser extensions), hardware wallets sign transactions on the device itself, meaning your private key never touches the internet.
Popular Hardware Wallet Brands
- Ledger Wallets
- Models: Ledger Nano S Plus, Ledger Nano X
- Supports 5,000+ coins and tokens
- Bluetooth-enabled (Nano X) for mobile use
- Trezor Wallets
- Models: Trezor Model One, Trezor Model T
- Open-source firmware
- Known for simple UI and robust support
- SafePal, Keystone, Coldcard – Also gaining traction among security-conscious users
How to Transfer Crypto to Ledger Nano X
Step-by-step transfer guide:
- Download Ledger Live on desktop or mobile
- Connect your Ledger Nano X via USB or Bluetooth
- Install the crypto app (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum) on the device
- Generate a receive address from Ledger Live
- Copy the address and paste it into the “send” field of your existing wallet or exchange
- Confirm the transaction on your Ledger device
Why Use a Hardware Wallet?
- Immune to online hacks
- Ideal for long-term storage
- Supports multiple assets
- Gives full ownership of your keys and funds
Hardware wallets are a crucial tool for any serious crypto investor, offering unmatched peace of mind in an unpredictable market.
Software and Mobile Wallets
A software or mobile wallet is a crypto wallet app that lets you manage, send, and receive digital assets on your phone or desktop. It’s easy to use and ideal for beginners. The best cryptocurrency mobile apps combine strong security, user-friendly design, and multi-coin support for managing crypto on the go.
Why Choose a Mobile or Software Wallet?
If you’re new to crypto or want fast access to your assets, a software or mobile wallet is often the best place to start. These wallets offer an intuitive interface and are perfect for managing small to medium holdings.
Advantages:
- Instant setup
- Easy access to funds
- Seamless dApp and NFT integration
- Often include in-app swaps, staking, and fiat purchases
Many users prefer mobile apps because they combine convenience with increasingly robust security features.
Safety Considerations: How to Keep Your Wallet Safe
Your crypto wallet may be mobile, but that doesn’t mean you should let your guard down. Even the best cryptocurrency mobile app can’t protect you from poor habits.
Here’s how to keep your wallet safe:
- Download apps only from verified sources (App Store, Google Play)
- Use biometric security or a strong PIN
- Never store your 12-word recovery phrase in your phone notes
- Turn off clipboard tracking permissions, especially on Android
- Use app-lock features for added security
Reminder: A mobile wallet is as safe as the phone it lives on—keep your OS updated and avoid installing apps from unknown sources.
Specialized Wallet Types
Not all wallets are built the same. Depending on how you use crypto—whether it’s for security, NFTs, DeFi, or multiple chains—you’ll want a wallet designed for your specific needs. Let’s clear up some common misconceptions and explain what’s out there.
What’s a Multi-Sig Wallet?
A multi-sig wallet (short for multi-signature wallet) requires more than one private key to authorize a transaction. Think of it like a joint bank account—no single party can move funds alone.
Why it matters:
Multi-sig wallets are used by crypto teams, DAOs, and security-conscious users who want to reduce the risk of theft or human error. Even if one key is compromised, the attacker can’t move your crypto without the others.
Myth busted:
Multi-sig doesn’t mean multiple wallets—it’s one wallet with shared control.
What Is a Self-Custody Wallet?
A self-custody wallet means you hold the private keys. It’s the opposite of keeping crypto on an exchange.
Why it matters:
If you’ve ever asked, “What is a self custody wallet and why should I care?”—here’s the answer: it gives you complete ownership and freedom. No third party can freeze, block, or access your funds.
Why You Need an NFT Wallet
An NFT wallet isn’t technically different—it’s just a wallet that supports NFT standards like ERC-721 or ERC-1155. You’ll want one that lets you view, send, and manage NFTs seamlessly.
Top picks:
- MetaMask
- Trust Wallet
- Deffio Wallet (NFT support planned in roadmap)
DeFi Wallet Requirements
If you’re diving into decentralized finance, you’ll need a DeFi wallet that interacts with smart contracts. These wallets must connect to Web3 dApps and support assets like ETH, stablecoins, and governance tokens.
Requirements:
- Browser extension or mobile dApp support
- Token swap features
- Compatibility with protocols like Uniswap, Aave, or Curve
Managing a Crypto Multi Wallet Setup
Using a crypto multi wallet strategy—separating wallets by purpose—is smart.
Example:
- One wallet for DeFi
- One cold wallet for storage
- One wallet for NFTs
This minimizes risk and improves organization.
Tip: Use a wallet dashboard app to track balances across all wallets in one place.
Wallet Security and Best Practices
Securing Your Crypto Assets
To secure cryptocurrency, use two-factor authentication, store assets in cold wallets, and back up your recovery phrase offline. Avoid phishing links and never share private keys. Cold storage of cryptocurrency is the safest long-term method, while 2FA crypto protections add an essential layer of access control.
How to Secure Cryptocurrency: A Layered Approach
Crypto security isn’t about one magic solution—it’s about layering defenses. Think of your crypto wallet like a vault. Would you protect it with just one lock? Probably not.
Here’s what matters most:
- Control your keys (self-custody)
- Isolate high-value funds (cold storage)
- Use authentication layers (2FA, biometrics)
- Back up your wallet safely (recovery phrase)
What Is 2FA in Crypto and Why It Matters
2FA crypto protection, or two-factor authentication, adds a second verification step to access your wallet or exchange account. It’s a must-have, especially for hot wallets and mobile apps.
Options for 2FA:
- Authenticator apps (e.g., Google Authenticator, Authy) – Recommended
- SMS codes – Less secure but better than nothing
- Hardware 2FA keys (e.g., YubiKey) – Ideal for advanced users
Cold Storage of Cryptocurrency: The Gold Standard
If you’re holding large amounts or long-term assets, cold storage is your best line of defense. This means keeping your private keys entirely offline—away from internet threats.
Cold storage options include:
- Hardware wallets (Ledger, Trezor)
- Paper wallets (written keys stored securely)
- Air-gapped devices (USB wallets never connected to the internet)
Backup Procedures: Your Last Line of Defense
Your wallet’s recovery phrase (usually 12 or 24 words) is the only way to regain access if you lose your device.
Best backup practices:
- Write the phrase on paper or metal (not digital)
- Store in a fireproof, waterproof location
- Consider using two geographically separate locations for redundancy
Understanding Wallet Vulnerabilities
Even the most secure wallets can be compromised if users overlook common threats. In this section, you’ll learn how hackers target crypto wallets through subtle tricks—often without you realizing it. We’ll break down essential vulnerabilities, including dust attacks, weak recovery phrase handling, and poor private key hygiene.
What Is a Dust Attack in Crypto?
A dust attack, also known as crypto dusting, is when attackers send tiny amounts of crypto to your wallet to track your transactions and potentially deanonymize your identity. The goal isn’t theft—it’s surveillance, usually followed by phishing or social engineering attempts.
How Dust Attacks Work:
Attackers send “dust”—fractions of coins like BTC or ETH—to thousands of wallets. If you interact with this dust (e.g., send it, consolidate funds), your wallet’s transactions can be analyzed using blockchain forensics tools.
Why it matters: Dusting often precedes targeted attacks. It’s not about the dust—it’s about you becoming a target.
Tip: If you receive an unknown crypto amount in your wallet, don’t touch it. Use a wallet with coin control features or mark dust as unspendable.
Recovery Phrase Risks (And How People Lose Everything)
Your recovery phrase is your last lifeline—but it’s also your weakest link if not protected. Whether you use MetaMask, Ledger, or Crypto.com, the recovery phrase gives full access to your wallet.
Common mistakes:
- Saving the phrase in cloud notes or screenshots
- Entering it into fake websites after phishing emails
- Using a “backup” service that isn’t secure or decentralized
Reminder: No legit service will ever ask for your recovery phrase—not even Deffio’s support team. That’s your private access code. Full stop.
Public Key Safety ≠ Private Key Safety
Public keys are meant to be shared—you need them to receive crypto. But your private keys are a different story. They must stay offline and encrypted.
Key vulnerabilities include:
- Keyloggers capturing clipboard data
- Fake browser extensions reading keys
- Brute force attacks on poorly encrypted backups
By understanding and avoiding these wallet vulnerabilities, you protect not just your crypto—but your identity, privacy, and peace of mind.
Storage Best Practices
The safest way to store crypto, especially Bitcoin, is with a hardware wallet or another form of cold storage. These methods keep your private keys offline, protecting you from online hacks. For active use, secure mobile apps with 2FA can work—but long-term holders need extra precautions.
How to Store Bitcoins Safely
If you’ve ever Googled “how to store bitcoins”, you’re already ahead of many crypto users. The right storage method depends on your risk tolerance, portfolio size, and usage frequency.
Here are the core methods:
- Mobile wallets (hot) – Great for small amounts and frequent use. Use a safe app like Trust Wallet, MetaMask, or Deffio’s upcoming VASP-compliant wallet for security and ease of use.
- Hardware wallets (cold) – Ideal for long-term holdings and large portfolios. They keep your private keys offline.
- Paper wallets – Not recommended for beginners due to technical risks and difficulty restoring.
Safest ways to store crypto: Combine hot and cold storage. Keep your spending funds in a hot wallet and your savings in a cold wallet.
Do I Need a Hardware Wallet?
It depends. If you hold over a few hundred dollars in crypto—and don’t plan to trade it daily—then yes, a hardware wallet is worth it. Think of it as buying a digital safe.
Hardware wallet benefits:
- Keeps keys offline and away from hackers
- Requires physical confirmation of every transaction
- Resistant to malware and phishing
- Works without depending on third-party platforms
“Hardware wallets offer peace of mind for anyone serious about safeguarding their digital assets,” says Deffio’s Head of Security. “If you wouldn’t leave your life savings in your phone’s notes app, don’t leave your crypto there either.”
Advanced Wallet Operations
Wallet Transactions and Transfers
Whether you’re making a quick payment with Bitcoin, sending funds to a cold wallet, or integrating a business checkout system, understanding crypto transactions is crucial.
How to Pay with Bitcoins
To pay with Bitcoins, you need the recipient’s wallet address or QR code. In your wallet app, enter the destination, input the amount, verify the fee, and confirm the transaction.
Voice Search Optimized Answer: To pay with Bitcoins, enter the recipient’s wallet address or scan their QR code in your wallet app, set the amount, and confirm. Always double-check the address before sending.
Modern wallets like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Deffio’s upcoming app allow one-tap payment confirmation, while businesses can use Deffio’s payment integration API for seamless crypto checkout, enabling real-time confirmation and automated invoice handling.
What Is a Destination Tag?
Certain cryptocurrencies like XRP, Stellar (XLM), and Cosmos (ATOM) require a destination tag or crypto memo. These identify the recipient within a shared address.
Pro Tip: If you’re sending to an exchange, not including the correct tag can result in permanent loss or a support ticket nightmare.
How to Transfer Crypto to Ledger Nano X
- Open Ledger Live
- Connect Ledger Nano X via USB/Bluetooth
- Install asset app (e.g., Bitcoin, ETH)
- Generate a receiving address
- Send funds from your current wallet
- Confirm on the device
Your assets are now in cold storage—offline and under your full control.
Trading and Swapping Within Wallets
In-wallet trading features are revolutionizing how users engage with crypto.
What Is Swapping Crypto?
Swapping crypto means exchanging one coin for another directly within your wallet—no separate exchange needed. Apps like Trust Wallet, MetaMask, and Deffio’s infrastructure support this via DEX (decentralized exchange) integrations.
Advanced Features and Custody Solutions
As portfolios grow, so does the need for institutional-grade custody.
What Is Crypto Custody?
Crypto custody refers to third-party services that securely store private keys and provide insurance, auditing, and compliance solutions—ideal for companies and high-net-worth individuals.
Fidelity-Style Custody for Whale Cryptocurrency Holders
Fidelity crypto custody and similar providers offer:
- Cold storage vaults
- Multisig access controls
- Regulatory compliance
- Asset insurance
These services are suited for whale cryptocurrency holders—those managing large portfolios needing professional protection.
Tracking Crypto Basis
Tracking crypto basis—the original purchase value—is essential for capital gains reporting. Wallets and custody providers like Deffio offer built-in tax reporting tools to help users manage this.
DeFi and Web3 Wallet Integration
DeFi Wallet Fundamentals
DeFi, or decentralized finance, lets users lend, borrow, swap, and earn interest—without banks.
What Is a DeFi Wallet?
A DeFi wallet connects to decentralized apps (dApps) like Aave, Compound, or Uniswap. These wallets offer Web3 capabilities, allowing direct interaction with smart contracts.
Voice Search Optimized Answer: A DeFi wallet is a crypto wallet that connects to decentralized apps and protocols, letting you earn, borrow, or swap assets without an intermediary.
Proof of Stake Participation
Many DeFi wallets support staking, enabling users to earn rewards by locking up tokens to validate blockchain transactions.
Yield Farming
DeFi wallets also allow yield farming—putting assets into liquidity pools to earn passive income. While profitable, it carries risks like impermanent loss and smart contract bugs.
Staking and Earning with Wallets
What Is Staking Crypto?
Staking crypto means locking coins in a wallet to support network operations (usually PoS) and earn rewards.
Voice Search Optimized Answer: Staking crypto lets you earn rewards by locking coins to support blockchain operations. It’s like earning interest on savings.
Popular wallets for staking:
- MetaMask (via Lido)
- Trust Wallet
- Deffio Wallet (enterprise staking services)
What Is an Airdrop?
A crypto airdrop is a free token distribution to wallet holders—usually as part of a promotion or DAO governance incentive. Holding the right tokens at the right time can result in surprising rewards.
Wallets that support staking and airdrops often include notification features so users don’t miss out.
Web3 and dApp Integration
Web3 wallets enable users to interact with decentralized applications directly.
What Are dApps?
dApps are decentralized applications built on blockchains. They include games, DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, and more.
Voice Search Optimized Answer: A dApp is a decentralized app that runs on a blockchain and works with crypto wallets to let users access DeFi, NFTs, and DAOs.
Smart Contract Interactions
Wallets like MetaMask and Deffio connect users to smart contracts—programs that automatically execute transactions. It’s how staking, borrowing, and token swaps happen trustlessly.
Crypto Wallet Ecosystem
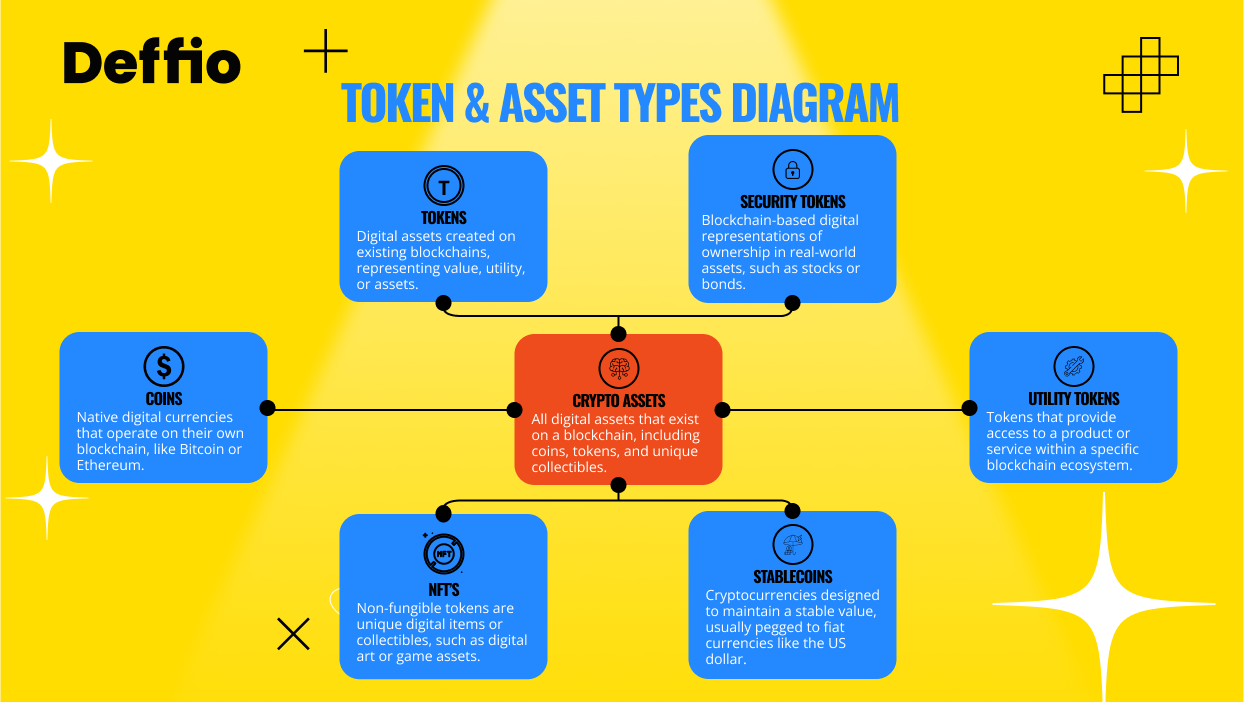
Tokens and Digital Assets
What Are Tokens?
Tokens are digital assets built on existing blockchains (like Ethereum). They can represent value, access, or governance rights.
- ERC-20: Fungible tokens (e.g., USDT, LINK)
- ERC-721: NFTs (e.g., Bored Ape, CryptoPunks)
Portfolio diversification means holding a mix of token types—across use cases and ecosystems.
Advanced Blockchain Features
What Is the Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network is a Layer 2 payment protocol that allows fast, low-cost Bitcoin transactions. It’s ideal for micro-payments and improves Bitcoin scalability.
What Are Hard Forks?
A hard fork occurs when a blockchain splits due to rule changes. Example: Bitcoin Cash forked from Bitcoin in 2017 due to scalability disagreements.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
What Is Crypto Gifting?
Crypto gifting lets users send digital assets to others as gifts or rewards. Some wallets and exchanges offer branded gifting features—Deffio is exploring such capabilities through its B2B wallet suite.
Cryptocurrency Ban Countries
Some countries restrict or ban crypto use—like China, Algeria, and Morocco. Others, like Portugal and Poland, are crypto-friendly but evolving. EU-wide VASP licensing (as adopted by Deffio) ensures regulatory compliance across borders.
Tax and Legal Considerations
Navigating the tax landscape around cryptocurrencies is essential if you want to stay compliant—and avoid unpleasant surprises down the line. Whether you’re a casual trader, long-term holder, or DeFi power user, understanding your crypto tax obligations is part of responsible crypto ownership.
Do You Pay Taxes on Crypto Before Withdrawal?
Yes, in most jurisdictions you pay taxes on crypto when you sell or convert it, regardless of whether you withdraw it to fiat or not.
This common question—”do you pay taxes on crypto before withdrawal?”—reveals a major misconception. You owe taxes when a taxable event occurs, such as:
- Selling crypto for fiat (USD, EUR, etc.)
- Swapping one crypto for another (e.g., BTC → ETH)
- Using crypto to pay for goods or services
Even if you never convert your crypto into fiat, most tax agencies still consider these actions taxable.
Crypto Tax Reporting: What to Know
Taxes for cryptocurrency vary by country but generally include:
- Capital gains taxes on profits from trading or investing
- Income tax if you’re earning crypto through staking, airdrops, or as payment
Key Reporting Practices:
- Track every transaction (apps like Koinly or CoinTracker help)
- Keep copies of all trades, wallet addresses, and values at the time of transaction
- Report staking and airdrop income at market value when received
Deffio’s infrastructure includes exportable transaction reports that support accounting tools and integrate with regional requirements.
How to Cash Out on Crypto.com (and Stay Compliant)
If you’re asking “how to cashout on crypto.com,” the process is straightforward: sell your crypto for fiat in the app and transfer the balance to your linked bank account. Remember, the sale itself is the taxable event—not the withdrawal.
Be sure to download your transaction history for each taxable year.
Geo-specific Notes
- Portugal: Finanças recently clarified that occasional crypto gains may be tax-exempt, but habitual trading or business activities are taxable.
- Poland: Cryptocurrency is taxed under capital gains rules; keeping meticulous records is crucial. Wallet-to-wallet transfers are not taxed unless a conversion occurs.
With evolving regulations and cross-border wallets, using Deffio’s VASP-compliant tools ensures your transactions are legally documented, secure, and audit-ready—no matter where you operate.
Always consult a licensed tax advisor for jurisdiction-specific guidance.
FAQ: Your Crypto Wallet Questions Answered
This section answers the top crypto wallet questions based on real user queries and search intent. Each FAQ is structured for FAQPage schema markup, optimized for “People Also Ask” results, and designed for performance via lazy-loaded, collapsible accordions.
1. What is a cryptocurrency wallet and how does it work?
A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool that stores your private keys and allows you to send, receive, and manage crypto. It doesn’t hold coins directly but gives you access to them on the blockchain. It works by signing transactions with your private key to prove ownership.
2. What’s the difference between hot and cold wallets?
Hot wallets are connected to the internet and best for daily use. Cold wallets are offline and used for long-term storage. Hot wallets are convenient but more vulnerable to hacking. Cold wallets offer better protection but require physical access.
3. Do I need a hardware wallet for crypto storage?
If you’re holding a significant amount of crypto or want long-term storage, yes. Hardware wallets keep your private keys offline and away from potential threats like malware and phishing attacks. They’re ideal for securing large balances.
4. How do I create my first crypto wallet?
Download a trusted wallet app (like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or Deffio), choose “Create Wallet,” back up your 12-word recovery phrase, set a PIN or password, and you’re ready to go. Always write down and secure your recovery phrase offline.
5. What are private keys and public keys?
Your public key is like your crypto address—it’s safe to share. Your private key is your secret code that proves ownership and authorizes transactions. If someone gets your private key, they can access your crypto. Never share it.
6. How do I secure my crypto wallet from hackers?
Use two-factor authentication (2FA), store large balances in cold wallets, never share your recovery phrase, and verify URLs before entering sensitive information. Use trusted apps only from verified sources.
7. What is a recovery phrase and why is it important?
A recovery phrase (usually 12 or 24 words) lets you restore your wallet if your device is lost or stolen. It’s a human-readable backup of your private key. If someone else gets it, they can take your crypto.
8. Can I use multiple crypto wallets?
Yes. Many users have multiple wallets for different purposes: one for DeFi, one for cold storage, one for NFTs. This is called a crypto multi wallet strategy and helps manage risk.
9. What is DeFi and how do I use DeFi wallets?
DeFi stands for decentralized finance. It includes apps like Uniswap and Aave that let you lend, borrow, and trade without intermediaries. DeFi wallets like MetaMask or Deffio connect directly to these protocols and let you interact with smart contracts.
10. How do I stake cryptocurrency from my wallet?
In a wallet that supports staking (like Trust Wallet or Deffio), select the crypto asset, choose “Stake,” enter the amount, and confirm. You’ll lock up tokens and earn rewards for helping secure the network.
11. What are the best crypto wallet apps for mobile?
Top options include:
- MetaMask: Best for DeFi and NFTs
- Trust Wallet: Supports 70+ blockchains
- Exodus: Great UX and multi-asset support
- Deffio App: Built for security and compliance, perfect for beginners and businesses
12. How do I transfer crypto between wallets?
Copy the receiving wallet address from your target wallet, paste it in the “send” section of your current wallet, enter the amount, confirm network fees, and complete the transfer. Always double-check addresses.
13. What is a dust attack and how do I protect myself?
A dust attack sends tiny crypto amounts to your wallet to analyze your activity and possibly deanonymize you. Don’t interact with unknown small balances. Use a wallet that supports coin control and track unusual transactions.
14. Do I pay taxes on crypto in my wallet?
You don’t pay taxes just for holding crypto, but you do when you trade, sell, or use it. Even swapping one token for another is a taxable event in many countries. Deffio’s wallet supports exportable transaction logs for tax reporting.
15. What happens if I lose access to my crypto wallet?
If you backed up your recovery phrase, you can restore your wallet on any compatible app. If you didn’t, the funds are permanently lost—there’s no “forgot password” option in decentralized wallets.
This FAQ is constantly updated to reflect changes in regulation, tech, and user concerns. For business users, Deffio offers scalable, compliant wallet infrastructure that includes audit-ready reporting, user access controls, and enterprise recovery protocols.